Python Slots
使用slots 但是,如果我们想要限制实例的属性怎么办?比如,只允许对Student实例添加name和age属性。 为了达到限制的目的,Python允许在定义class的时候,定义一个特殊的slots变量,来限制该class实例能添加的属性:. Monty Python and the Holy Grail Slots. Having figured out the Meaning of Life, and having had us racing through the hectic Life of Brian, it’s time us diehard real cash slot fans play Monty Python and the Holy Grail. In contrast, a class instance with slots declared to be (no data) is only 16 bytes, and 56 total bytes with one item in slots, 64 with two. For 64 bit Python, I illustrate the memory consumption in bytes in Python 2.7 and 3.6, for slots and dict (no slots defined) for each point where the dict grows in 3.6 (except for 0, 1, and 2.
Signals are a neat feature of Qt that allow you to pass messages between different components in your applications.
Signals are connected to slots which are functions (or methods) which will be run every time the signal fires. Many signals also transmit data, providing information about the state change or widget that fired them. The receiving slot can use this data to perform different actions in response to the same signal.
However, there is a limitation: the signal can only emit the data it was designed to. So for example, a QAction has a .triggered that fires when that particular action has been activated. The triggered signal emits a single piece of data -- the checked state of the action after being triggered.
For non-checkable actions, this value will always be False
The receiving function does not know whichQAction triggered it, or receiving any other data about it.
This is usually fine. You can tie a particular action to a unique function which does precisely what that action requires. Sometimes however you need the slot function to know more than that QAction is giving it. This could be the object the signal was triggered on, or some other associated metadata which your slot needs to perform the intended result of the signal.
This is a powerful way to extend or modify the built-in signals provided by Qt.
Intercepting the signal
Instead of connecting signal directly to the target function, youinstead use an intermediate function to intercept the signal, modify the signal data and forward that on to your actual slot function.
This slot function must accept the value sent by the signal (here the checked state) and then call the real slot, passing any additional data with the arguments.
Rather than defining this intermediate function, you can also achieve the same thing using a lambda function. As above, this accepts a single parameter checked and then calls the real slot.
In both examples the <additional args> can be replaced with anything you want to forward to your slot. In the example below we're forwarding the QAction object action to the receiving slot.
Our handle_trigger slot method will receive both the original checked value and the QAction object. Or receiving slot can look something like this
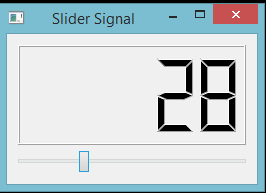
Below are a few examples using this approach to modify the data sent with the MainWindow.windowTitleChanged signal.
- PyQt5
- PySide2
The .setWindowTitle call at the end of the __init__ block changes the window title and triggers the .windowTitleChanged signal, which emits the new window title as a str. We've attached a series of intermediate slot functions (as lambda functions) which modify this signal and then call our custom slots with different parameters.
Running this produces the following output.
Python Slots Example
The intermediate functions can be as simple or as complicated as you like -- as well as discarding/adding parameters, you can also perform lookups to modify signals to different values.
In the following example a checkbox signal Qt.Checked or Qt.Unchecked is modified by an intermediate slot into a bool value.
- PyQt5
- PySide2
In this example we've connected the .stateChange signal to result in two ways -- a) with a intermediate function which calls the .result method with True or False depending on the signal parameter, and b) with a dictionary lookup within an intermediate lambda.
Running this code will output True or False to the command line each time the state is changed (once for each time we connect to the signal).
QCheckbox triggering 2 slots, with modified signal data
Trouble with loops
One of the most common reasons for wanting to connect signals in this way is when you're building a series of objects and connecting signals programmatically in a loop. Unfortunately then things aren't always so simple.
If you try and construct intercepted signals while looping over a variable, and want to pass the loop variable to the receiving slot, you'll hit a problem. For example, in the following code we create a series of buttons, and use a intermediate function to pass the buttons value (0-9) with the pressed signal.
Slot Machine In Python
- PyQt5
- PySide2
If you run this you'll see the problem -- no matter which button you click on you get the same number (9) shown on the label. Why 9? It's the last value of the loop.
The problem is the line lambda: self.button_pressed(a) where we pass a to the final button_pressed slot. In this context, a is bound to the loop.
We are not passing the value of a when the button is created, but whatever value a has when the signal fires. Since the signal fires after the loop is completed -- we interact with the UI after it is created -- the value of a for every signal is the final value that a had in the loop: 9.
So clicking any of them will send 9 to button_pressed
The solution is to pass the value in as a (re-)named parameter. This binds the parameter to the value of a at that point in the loop, creating a new, un-connected variable. The loop continues, but the bound variable is not altered.
This ensures the correct value whenever it is called.
You don't have to rename the variable, you could also choose to use the same name for the bound value.
Python Slots Dataclass
The important thing is to use named parameters. Putting this into a loop, it would look like this:
Running this now, you will see the expected behavior -- with the label updating to a number matching the button which is pressed.
The working code is as follows:
Python __slots__
- PyQt5
- PySide2



